
It is structured systematically to lay out the capital spending made from the investments.

Currently an investment analyst focused on the TMT sector at 1818 Partners (a New York Based Hedge Fund), Sid previously worked in private equity at BV Investment Partners and BBH Capital Partners and prior to that in investment banking at UBS.
Sid holds a BS from The Tepper School of Business at Carnegie Mellon.
Reviewed By: Hassan Saab
Prior to becoming a Founder for Curiocity, Hassan worked for Houlihan Lokey as an Investment Banking Analyst focusing on sellside and buyside M&A , restructurings, financings and strategic advisory engagements across industry groups.
Hassan holds a BS from the University of Pennsylvania in Economics.
Last Updated: October 24, 2023 In This ArticleA proceeds statement is a statement where the expenditures are explained to the investors. It is structured systematically to lay out the capital spending made from the investments.
Use of proceeds statement is used majorly by start-ups seeking funds; the document is short and doesn’t usually exceed more than two pages.
The numbers added on proceeds statements are tentative estimations and are usually averaged to the nearest millions or thousands.
The proceeds statement or document is usually added to other business documents, such as annual business planning, etc., where a section describes the tentative funding.
Venture capitalists or Angel investors usually seek the use of proceeds statements or documents whenever a young start-up or entrepreneur makes an investment proposal.
Other than start-ups or individual businesses, the use proceeds statements are also used by big companies and corporations when they plan to go public, usually during their IPOs (Initial public offerings).
Using a proceeds statement can be beneficial while raising capital as the investors know where the money is being allocated to and can better model the company on what it is valued at and how it might perform.
A good use of a proceeds statement can increase the chance of investments. On the other hand, wrong “use of a proceeds statement,” failing to allocate net required capital can drastically impact invested capital .
There are two main ways the proceeds statement is formatted, usually in wording or a graph describing each expense ratio by percentage or numeric.
The proceeds statement is just a simple chart of expenses rather than a predictive forecast like any model. Let us differentiate these two to see if either provides any advantage.
1. Written
A written summary of the use of proceeds statement is usually added in financial documents describing the areas where the capital will be spent.
The statement starts with the net proceeds, and the rest expenses add up to less than or equal to the net proceeds.
The difference between the net proceeds and total expenditures accounts for the issuance of shares and other expenses.
| Net Proceeds | $100,000 |
|---|---|
| R&D | $40,000 |
| Marketing | $50,000 |
| $90,000 |
As given in the example, the total research and development expenditures are 90,000, 10,000 less than the net proceeds.
2. Chart
The proceeds statement in a chart form is usually used in the presentation case to simplify the expenditures.
The form of the chart is not specific and depends on the presentation's author.
A chart summing the values is usually preferred, like a pie chart.
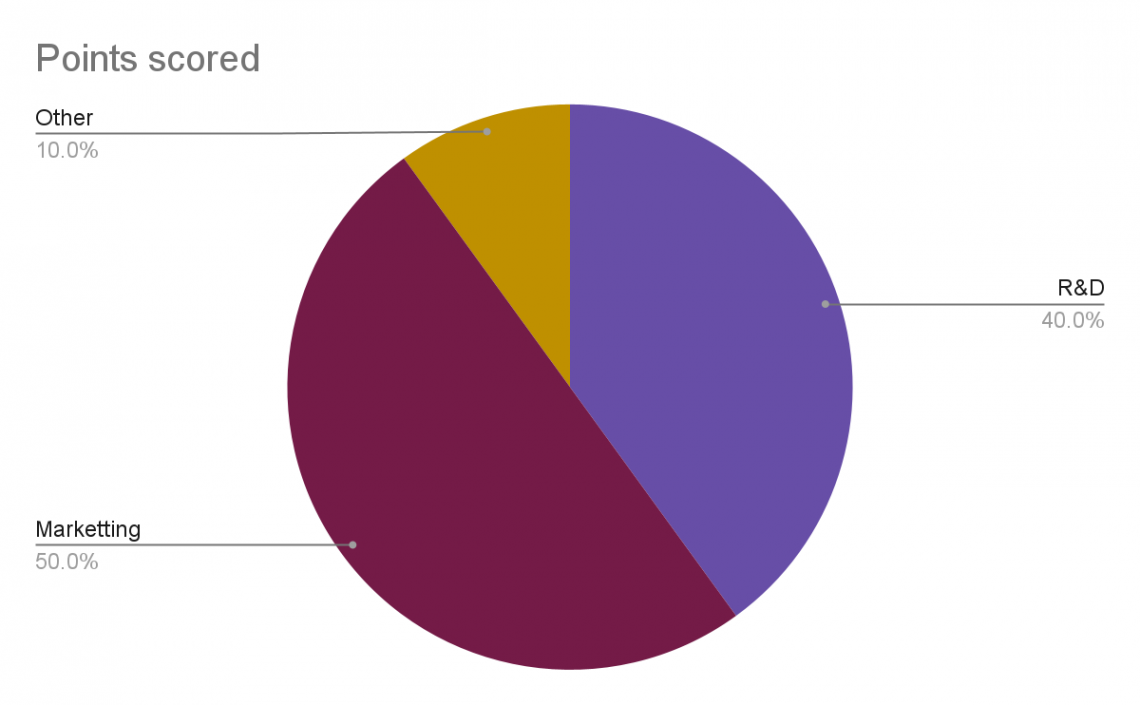
The same statement is presented through a chart that is better understood.
A proceeds statement is an important filing while releasing an IPO as it gives an overview to the potential investors in the company of what the invested capital will be used in.
Some companies prefer to keep their investments private from competitors as the statement might reveal their future plans for the company and their products or services.
To counter this, a company could follow a general corporate purpose format which includes the necessary allocations of the IPO funds such as working capital, operating expenses, and capital expenditures.
General corporate purpose is vague and doesn't provide investment details that detailed use of proceeds statement otherwise would.
Detailed use of proceeds statement highlights multiple sections, including