Fiscal Policy - Analysing and Evaluating Expansionary Fiscal Policy
In this revision video we focus on the economics of an expansionary fiscal policy.
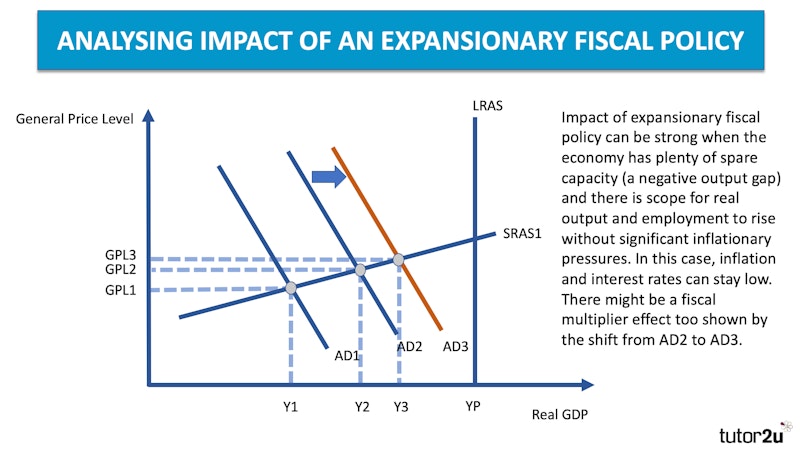
Evaluation: What factors influence whether an expansionary fiscal policy will achieve its objectives?
The macroeconomic impacts of an expansionary fiscal policy depends in part on
- Whether an expansionary fiscal policy leads to higher market interest rates for example if bond yields rise as a budget deficit increases (see ‘crowding-out’)
- Whether expansionary fiscal policies lead to an acceleration in the rate of price inflation which then cuts real incomes and spending by households
- The marginal propensity tospendandsaveofhouseholds. Will people spend or save an income tax cut? Or will they use it to repay existing debts.
- The marginalpropensity toimport – rising disposable incomes might feed through to increasing demand for imports and a widening net trade deficit.
- Whether expansionary fiscal policy leads to a riseinbusiness confidence
The impact of an expansionary fiscal policy depends on what else is happening in the economy. It also depends on the timing of the fiscal stimulus and the size of the injection of demand into the circular flow – measured as a share of GDP.

This is a great topic to bring in different schools of economic thought. For example, a Keynesian perspective (which favours using a fiscal stimulus when an economy is stuck in a liquidity trap) versus crowding out theorists who argue that higher spending and borrowing raises interest rates and squeeze out private sector investment.
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Twitter
- Share by Email



