Incomplete dominance is a form of Gene interaction in which both alleles of a gene at a locus are partially expressed, often resulting in an intermediate or different phenotype. It is also known as partial dominance.
For eg., in roses, the allele for red colour is dominant over the allele for white colour. But, the heterozygous flowers with both the alleles are pink in colour.
Incomplete dominance occurs because neither of the two alleles is completely dominant over the other. This results in a phenotype that is a combination of both.
Gregor Mendel conducted experiments on pea plants. He studied on seven characters with contrasting traits and all of them showed a similar pattern of inheritance. Based on this, he generalized the law of inheritance.
Later, researchers repeated Mendel’s experiment on other plants. Shockingly, they noted that the F1 Generation showed variation from the usual pattern of inheritance. The monohybrid cross resulted in F1 Progeny which didn’t show any resemblance to either of the parents, but an intermediate progeny.
Let’s understand the incomplete dominance with the example of Snapdragon flower (Antirrhinum sp).

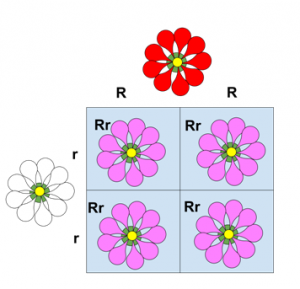
Monohybrid cross was done between the red and white coloured flowers of Snapdragon plant. Consider, pure breed of the red flower has RR pair of alleles and that for the white flower is rr.
Firstly, true-breeding red (RR) and white (rr) coloured flowers of snapdragon were crossed. The F1 generation produced a pink coloured flower with Rr pair of alleles.
Then the F1 progeny was self-pollinated. This resulted in red (RR), pink (Rr) and white (rr) flowers in the ratio of 1:2:1.
Recollect that the genotype ratio of F2 generation in the monohybrid cross by Mendel also gave the same ratio of 1:2:1. However, the phenotype ratio has changed from 3:1 to 1:2:1. The reason for this variation is the incomplete dominance of the allele R over the allele r. This led to the blending of colour in flowers.
In genetics, Dominance is a relationship between alleles of one gene. In order to understand the concept of the dominance of alleles, we need to know more about genes.
So far we know that genes are a hereditary unit in organisms which exist as a pair of alleles in diploid organisms. These pair of alleles may or may not be similar. That is, a heterozygous gene has two dissimilar pairs of alleles while homozygous have identical ones.
Heterozygous alleles carry different information on traits. When we say one trait is dominant over the other, there can be two reasons:
Incomplete dominance and codominance are different from each other.
In codominance, both the alleles present on a gene are expressed in the phenotype. A flower showing codominance will have patches of red and white instead of a uniformly pink flower.
In incomplete dominance, the F2 generation from heterozygous plants will have a ratio of 1:2:1 with the phenotypes red, white and spotted flowers.
The humans with AB blood type also show codominance where the alleles for both blood types A and B are expressed.
Examples of incomplete dominance are mentioned below:
The child of parents each with curly hair and straight hair will always have wavy hair. Carriers of Tay-Sachs disease exhibit incomplete dominance.
The Andalusian chicken shows incomplete dominance in its feather colour.
When the rabbits with long and short furs are bred, the offsprings produced will have medium fur length.
For more details on incomplete dominance, dominance and incomplete dominance and codominance, keep visiting BYJU’S website or download BYJU’S app for further reference.
Test your knowledge on Incomplete Dominance